Abstract
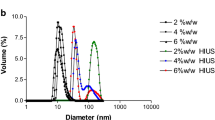
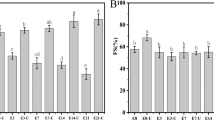
The objective of this research was to investigate the impact of high-intensity ultrasound (HIU) generated by a probe-type sonicator (frequency 20 ± 0.2 kHz and an amplitude of 40%) for 2–20 min on the selected functional and structural properties of egg white proteins (EWPs) and their susceptibility to hydrolysis by alcalase. The protein solubility, foaming, and emulsifying properties were studied as a function of ultrasonication time and related to protein particle and structural properties. The length of ultrasonication exhibited important effect on EWP particle size, uniformity, and charge, affecting also the protein conformation and susceptibility to alcalase hydrolysis and determining functional properties. There was a linear correlation between the particle size decrease and the solubility while a two-step linear correlation between the foam capacity (FC)/foam stability (FS) and particle size was apparent. Specifically, FC and FS sharply increased with decreasing particle size for range from ∼370 to ∼260 nm, and below this range from 260.6 to 68.4 nm, the changes were not that substantial. Besides, the solubility, FC, and FS were directly and linearly related with the absolute value of the particle zeta potential. The overall emulsifying properties were also improved with an increase of sonication time, through both the decrease of the mean particle diameter and the increase of zeta potential, but there was no direct correlation between the emulsion activity/stability index and protein particle size and/or charge. Analysis of EWP structure by Raman spectroscopy revealed that the HIU leads to changes in the secondary structure, while heat and ultrasound generated by the ultrasound bath were not sufficient to exhibit this effect.

Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler-Nissen, J. (1986). Enzymic hydrolysis of food proteins. London: Elsevier Applied Science Publishers.
Arzeni, C., Martinez, K., Zema, P., Arias, A., Perez, O. E., & Pilosof, A. M. R. (2012b). Comparative study of high intensity ultrasound effects on food proteins functionality. Journal of Food Engineering, 108, 463–472.
Arzeni, C., Pérez, O. E., & Pilosof, A. M. R. (2012a). Functionality of egg white proteins as affected by high intensity ultrasound. Food Hydrocolloids, 29, 308–316.
Barukčić, I., Lisak Jakopović, K., Herceg, Z., Karlović, S., & Božanić, R. (2015). Influence of high intensity ultrasound on microbial reduction, physico-chemical characteristics and fermentation of sweet whey. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technology, 27, 94–101.
Chandrapala, J., Zisu, B., Palmer, M., Kentish, S., & Ashokkumar, M. (2010). Effects of ultrasound on the thermal and structural characteristics of proteins in reconstituted whey protein concentrate. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 18, 951–957.
Chandrapala, J., Zisu, B., Kentish, A., & Ashokkumar, M. (2012). The effects of high-intensity ultrasound on the structural and functional properties of α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin and their mixtures. Food Research International, 48, 940–943.
Chen, D. (2012). Applications of ultrasound in water and wastewater treatment. In D. Chen, S. K. Sharma, & A. Mudhoo (Eds.), Handbook on application of ultrasound: sonochemistry for sustainability. Florida: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group.
Chi, Z., Chen, X. G., Holtz, J. S. W., & Asher, S. A. (1999). UV resonance Raman-selective amide vibrational enhancement: quantitative methodology for determining protein secondary structure. Biochemistry, 37, 2854–2864.
Dojcinovic, M., & Volkov-Husovic, T. (2008). Cavitation damage of the medium carbon steel: implementation of image analysis. Materials Letters, 62, 953–956.
Frydenberg, R. P., Hammershшj, M., Andersen, U., Greve, M. T., & Wiking, L. (2016). Protein denaturation of whey protein isolates (WPIs) induced by high intensity ultrasound during heat gelation. Food Chemistry, 192, 415–423.
Gulseren, I., Guzey, D., Bruce, B. D., & Weiss, J. (2007). Structural and functional changes in ultrasonicated bovine serum albumin solutions. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 14, 173–183.
Hu, H. Y., & Du, H. N. (2000). α-to-β structural transformation of ovalbumin: heat and pH effects. Journal of Protein Chemistry, 19, 177–183.
Hu, H., Fan, X., Zhou, Z., Xu, X., Fan, G., Wang, L., Huang, X., Pan, S., & Zhu, L. (2013). Acid-induced gelation behavior of soybean protein isolate with high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatments. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20, 187–195.
Huang, H., Kwok, K.-C., & Liang, H.-H. (2008). Inhibitory activity and conformation changes of soybean trypsin inhibitors induced by ultrasound. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 15, 724–730.
Jambrak, A. R., Lelas, V., Mason, T. J., Krešić, G., & Badanjak, M. (2009). Physical properties of ultrasound treated soy proteins. Journal of Food Engineering, 93, 386–393.
Kimura, T., Sakamoto, T., Leveque, J.-M., Sohmiya, H., Fujita, M., Ikeda, S., & Ando, T. (1996). Standardization of ultrasonic power for sonochemical reaction. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 3, S157.
Lai, K. M., Chuang, Y. S., Chou, Y. C., Hsu, Y. C., Cheng, Y. C., Shi, C. Y., Chi, Y., & Hsu, K. C. (2010). Changes in physicochemical properties of egg white and yolk proteins from duck shell eggs due to hydrostatic pressure treatment. Poultry Science, 89, 729–737.
Lei, B., Majumder, K., Shen, S., & Wu, J. (2011). Effect of sonication on thermolysin hydrolysis of ovotransferrin. Food Chemistry, 124, 808–815.
Li, K., Kang, Z.-L., Zhao, Y.-Y., Xu, X.-L., & Zhou, G.-H. (2014). Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve functional properties of batter suspension prepared from PSE-like chicken breast meat. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 3466–3477.
Li-Chan, E. C. Y. (1997). The application of Raman spectroscopy in food science. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 7, 361–370.
Mason, T. J. (2015). Some neglected or rejected paths in sonochemistry—a very personal view. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 25, 89–93.
Mason, T. J., Lorimer, J. P., & Bates, D. M. (1992). Quantifying sonochemistry: casting some light on a ‘black art’. Ultrasonics, 30, 40–42.
Mine, Y. (1995). Recent advances in the understanding of egg white protein functionality. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 6, 225–232.
Mine, Y. (1997). Effect of dry heat and mild alkaline treatment on functional properties of egg white proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45, 2924–2928.
Mine, Y., Tatsushi, N., & Haga, N. (1990). Thermally induced changes in egg white proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 38, 2122–2125.
Mirmoghtadaie, L., Aliabadi, S. S., & Hosseini, S. M. (2016). Recent approaches in physical modification of protein functionality. Food Chemistry, 199, 619–627.
Nawrocka, A., Szymańska-Chargot, M., Miś, A., Ptaszyńska, A. A., Kowalski, R., Waśkoa, P., & Gruszecki, W. I. (2015). Influence of dietary fibre on gluten proteins structure—a study on model flour with application of FT-Raman spectroscopy. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 46, 309–316.
Ngarize, S., Adams, A., & Howell, N. K. (2004). Studies on egg albumen and whey protein interactions by FT-Raman spectroscopy and rheology. Food Hydrocolloids, 18, 49–59.
O’Sullivan, J., Murray, B., Flynn, C., & Norton, I. (2016). The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins. Food Hydrocolloids, 53, 141–154.
Ozuna, C., Paniagua-Martínez, I., Castaño-Tostado, E., Ozimek, L., & Amaya-Llano, S. L. (2015). Innovative applications of high-intensity ultrasound in the development of functional food ingredients: production of protein hydrolysates and bioactive peptides. Food Research International, 77, 685–696.
Painter, P. C., & Koenig, J. L. (1976). Raman spectroscopic study of the proteins of egg white. Biopolymers, 15, 2155–2166.
Pearce, K. N., & Kinsella, J. E. (1978). Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 26(3), 716–723.
Shaw, D. L. (1992). Introduction to colloid and surface chemistry (pp. 174–199). London: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Shimada, K., & Cheftel, J. C. (1988). Determination of sulfhydryl groups and disulfide bonds in heat-induced gels of soy protein isolate. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 36, 147–153.
Stathopulos, P. B., Scholz, G. A., Hwang, Y.-M., Rumfeldt, J. A. O., Lepock, J. R., & Meiering, E. M. (2004). Sonication of proteins causes formation of aggregates that resemble amyloid. Protein Science, 13, 3017–3027.
Stefanović, A. B., Jovanović, J. R., Grbavčić, S. Ž., Šekuljica, N. Ž., Manojlović, V. B., Bugarski, B. M., & Knežević-Jugović, Z. D. (2014). Impact of ultrasound on egg white proteins as a pretreatment for functional hydrolysates production. European Food Research Technology, 239, 979–993.
Tan, M. C., Chin, N. L., Yasof, Y. A., Taip, F. S., & Abdullah, J. (2015). Improvement of eggless cake structure using ultrasonically treated whey protein. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 605–614.
Tavano, O. L. (2013). Protein hydrolysis using proteases: an important tool for food biotechnology. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 90, 1–11.
Tian, H., Xu, G., Yang, B., & Guo, G. (2011). Microstructure and mechanical properties of soy protein/agar blend films: effect of composition and processing methods. Journal of Food Engineering, 107, 21–26.
Tian, J., Wang, Y., Zhu, Z., Zeng, Q., & Xin, M. (2015). Recovery of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) protein isolate by high-intensity ultrasound-aided alkaline isoelectric solubilization/precipitation process. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8, 758–769.
Tiwari, B. K., & Mason, T. J. (2012). Ultrasound processing of fluid foods. In P. J. Cullen, B. K. Tiwari, & V. P. Valdramidis (Eds.), Novel thermal and non-thermal technologies for fluid foods (pp. 135–157). New York: Elsevier Academic Press.
Van der Plancken, I., Van Loey, A., & Hendrickx, M. E. (2005). Combined effect of high pressure and temperature on selected properties of egg white proteins. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 6, 11–20.
Van der Plancken, I., Van Loey, A., & Hendrickx, M. E. (2007). Foaming properties of egg white proteins affected by heat or high pressure treatment. Journal of Food Engineering, 78, 1410–1426.
Xiong, W., Wang, Y., Zhang, C., Wan, J., Shah, B. R., Pei, Y., Zhou, B., Li, J., & Li, B. (2016). High intensity ultrasound modified ovalbumin: structure, interface and gelation properties. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 31, 302–309.
Yanjun, S., Jianhang, C., Shuwen, Z., Hongjuan, L., Jing, L., Uluko, H., Yanling, S., Wenming, C., Wupeng, G., & Jiaping, L. (2014). Effect of power ultrasound pre-treatment on the physical and functional properties of reconstituted milk protein concentrate. Journal of Food Engineering, 124, 11–18.
Zhang, P., Hua, T., Feng, S., Xua, Q., Zheng, T., Zhou, M., Chu, X., Huang, X., Lu, X., Pan, S., Li-Chan, E. C. Y., & Hua, H. (2016a). Effect of high intensity ultrasound on transglutaminase-catalyzed soy protein isolate cold set gel. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 29, 380–387.
Zhang, Z., Arrighi, V., Campbell, L., Lonchamp, J., & Euston, S. R. (2016b). Properties of partially denatured whey protein products: formation and characterization of structure. Food Hydrocolloids, 52, 95–105.
Zhou, M., Liu, J., Zhou, Y., Huang, X., Liu, F., Pan, S., & Hu, H. (2016). Effect of high intensity ultrasound on physicochemical and functional properties of soybean glycinin at different ionic strengths. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technology, 34, 205–213.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to extend their appreciation to the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia for their financial support within the EUREKA Project E!6750 and Project III-46010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1
The emulsion activity/stability index of 2 wt. % ovalbumin treated with high-intensity ultrasound probe for various times (2, 5, 10, 15 and 20 min) at 20±0.2 kHz (GIF 222 kb)
Online Resource 2
Correlations between EAI and ESI and particle size (a) and zeta potential (b) of UPT ovalbumin solution (GIF 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stefanović, A.B., Jovanović, J.R., Dojčinović, M.B. et al. Effect of the Controlled High-Intensity Ultrasound on Improving Functionality and Structural Changes of Egg White Proteins. Food Bioprocess Technol 10, 1224–1239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1884-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1884-5